What are the Medicare Part D abbreviations: EA BA DS AE in the plan benefit type?
Medicare drug coverage offered by stand-alone Medicare Part D prescription drug plans (PDPs) and Medicare Advantage plans that offer drug coverage (MAPDs) can be categorized according to how the plan's coverage conforms to (or deviates from) the government's standard defined Medicare Part D definition (for example, does the Medicare drug plan have a standard initial deductible, fixed 25% cost-sharing, and standard Initial Coverage Limit).
As background, each year the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) releases a set of parameters for the standard defined Medicare drug plan coverage and a Medicare plan that follows this CMS model are termed defined standard (DS) drug plans. Medicare drug plans that are equivalent to the CMS defined standard Part D benefit are termed actuarially equivalent (AE) standard or basic alternative (BA). Medicare drug plans that exceed or deviate from the defined CMS standard coverage are termed enhanced alternative (EA) Medicare drug plans.
More about how to define the different plan types.
CMS adds the following summary of the different types of Medicare plans:
Why plan design is important: Medicare drug plan design affects Medicare Part D Extra Help benefits (or Low-Income Subsidy).
If you are qualified for the Medicare Part D Extra Help program, the cost of your monthly Medicare Part D premiums will be covered up to a certain level – called your state’s Low-Income Subsidy (LIS) Benchmark Premium. For example, if you live in a state with a benchmark premium of $25, the Medicare Part D Extra Help program will pay for your monthly premium up to this $25 level (or slightly above) and you will have a $0 premium when you enroll in a "basic" Medicare Part D plan with a premium around $25 or lower.
Important: However, if your chosen Medicare Part D plan's monthly premium has enhanced features (such as an EA Part D plan), you can be charged the amount of the monthly premium that exceeds the benchmark - or the portion of the premium that covered the cost of the enhanced features.
In our Frequently Asked Question "I am qualified for Medicaid and Medicare, so why am I still paying a monthly premium for my Part D drug plan?", we show examples of how a person with Extra Help benefits who enrolls in a low-costing Medicare Part D plan still is charged a partial monthly premium.
Example #1: In our first example, when a person has chosen to enroll into a Medicare Part D prescription drug plan that offers "enhanced" features - the person may find that the Part D plan does not qualify for the $0 monthly Low-Income Subsidy (LIS) premium.
Using California as our example state having a 2024 $40.98 LIS benchmark premium, and you qualify for Extra Help benefits, and decide to join the 2024 Wellcare Value Script (PDP) - you might expect to pay $0 because the WellCare Value Script plan only has a $0.40 premium - well below the 2024 California benchmark premium of $40.98.
However, as shown on our our PDP-Finder plan details page, if you were qualified for the Medicare LIS program, you would actually pay the monthly premium of $0.40 because the plan has "enhanced" features and does not qualify for the $0 premium even though the $0.40 premium is well below the state's $40.98 LIS $0 premium benchmark.

As background, each year the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) releases a set of parameters for the standard defined Medicare drug plan coverage and a Medicare plan that follows this CMS model are termed defined standard (DS) drug plans. Medicare drug plans that are equivalent to the CMS defined standard Part D benefit are termed actuarially equivalent (AE) standard or basic alternative (BA). Medicare drug plans that exceed or deviate from the defined CMS standard coverage are termed enhanced alternative (EA) Medicare drug plans.
More about how to define the different plan types.
CMS adds the following summary of the different types of Medicare plans:
"These terms were intended to provide explicit guidance on permissible benefit design parameters for [Medicare Part D prescription drug plan] sponsors and actuaries. The first three benefit types are considered basic prescription drug coverage, and are actuarially equivalent to the defined standard benefit established in statute. These basic benefit designs vary only in terms of whether cost sharing tiers are applied versus one level of coinsurance, the deductible is lowered or eliminated, and the initial coverage limit is increased."The information paraphrased below is from Chapter 5 of CMS Publication 100-18 Medicare Prescription Drug Benefit Manual which gives more details regarding the Medicare Part D benefit types:
- Defined standard (DS) benefits
A Medicare Part D plan that has an annual deductible, has 25% coinsurance in the initial coverage phase, receives only the 75% donut hole discount in the coverage gap. The features of the standard defined plan are updated and released annually by CMS: q1medicare.com/PartD-The-MedicarePartDOutlookAllYears.php
- Actuarially equivalent (AE) standard benefits
A Medicare Part D plan that has an annual deductible, the plan may substitute certain cost-sharing requirements in defined standard coverage including tiered structures tied to plan formularies or preferred pharmacies in a plan's network.
- Basic alternative (BA) benefits
A Medicare Part D plan that may have a reduced or $0 deductible, can use tiered co-payments or coinsurance, may have a modification to the initial coverage limit. Remains actuarially equivalent to the standard benefit.
- Enhanced alternative (EA) coverage
A Medicare Part D plan whose value exceeds that of the defined standard coverage. The plan design includes the basic prescription drug coverage and has supplemental benefits which may include: a reduction in cost-sharing in the "coverage gap" in addition to the donut discount, a reduction in or elimination of the initial deductible, a reduction in the coinsurance or co-payments applicable during the initial coverage phase, an increase in the initial coverage limit, and/or supplemental drugs.
Why plan design is important: Medicare drug plan design affects Medicare Part D Extra Help benefits (or Low-Income Subsidy).
If you are qualified for the Medicare Part D Extra Help program, the cost of your monthly Medicare Part D premiums will be covered up to a certain level – called your state’s Low-Income Subsidy (LIS) Benchmark Premium. For example, if you live in a state with a benchmark premium of $25, the Medicare Part D Extra Help program will pay for your monthly premium up to this $25 level (or slightly above) and you will have a $0 premium when you enroll in a "basic" Medicare Part D plan with a premium around $25 or lower.
Important: However, if your chosen Medicare Part D plan's monthly premium has enhanced features (such as an EA Part D plan), you can be charged the amount of the monthly premium that exceeds the benchmark - or the portion of the premium that covered the cost of the enhanced features.
In our Frequently Asked Question "I am qualified for Medicaid and Medicare, so why am I still paying a monthly premium for my Part D drug plan?", we show examples of how a person with Extra Help benefits who enrolls in a low-costing Medicare Part D plan still is charged a partial monthly premium.
Example #1: In our first example, when a person has chosen to enroll into a Medicare Part D prescription drug plan that offers "enhanced" features - the person may find that the Part D plan does not qualify for the $0 monthly Low-Income Subsidy (LIS) premium.
Using California as our example state having a 2024 $40.98 LIS benchmark premium, and you qualify for Extra Help benefits, and decide to join the 2024 Wellcare Value Script (PDP) - you might expect to pay $0 because the WellCare Value Script plan only has a $0.40 premium - well below the 2024 California benchmark premium of $40.98.
However, as shown on our our PDP-Finder plan details page, if you were qualified for the Medicare LIS program, you would actually pay the monthly premium of $0.40 because the plan has "enhanced" features and does not qualify for the $0 premium even though the $0.40 premium is well below the state's $40.98 LIS $0 premium benchmark.

Example #2: If you qualify for Extra Help and enrolled in a "basic" Medicare Part D plan with a premium below (or slightly over) the benchmark, you would pay a $0 premium. So if you chose the 2024 California Wellcare Classic (PDP) Medicare Part D plan that has a $35.90 premium, you would pay a $0 premium - since California has a $40.98 LIS benchmark premium.

However, in the same situation, if you enrolled in the 2024 California AARP MedicareRx Saver Plus (PDP) that has a $89.80 premium, you would pay $48.80 per month premium (roughly the $89.80 premium - the $40.98 benchmark premium).

Pre-2024 - A bit of Medicare Part D history... Full and Partial-LIS Benefits
Prior to plan year 2024, Medicare beneficiaries may have only received partial-LIS. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) expanded the Extra Help program to provide full-LIS benefits to people who formerly only received partial-LIS.
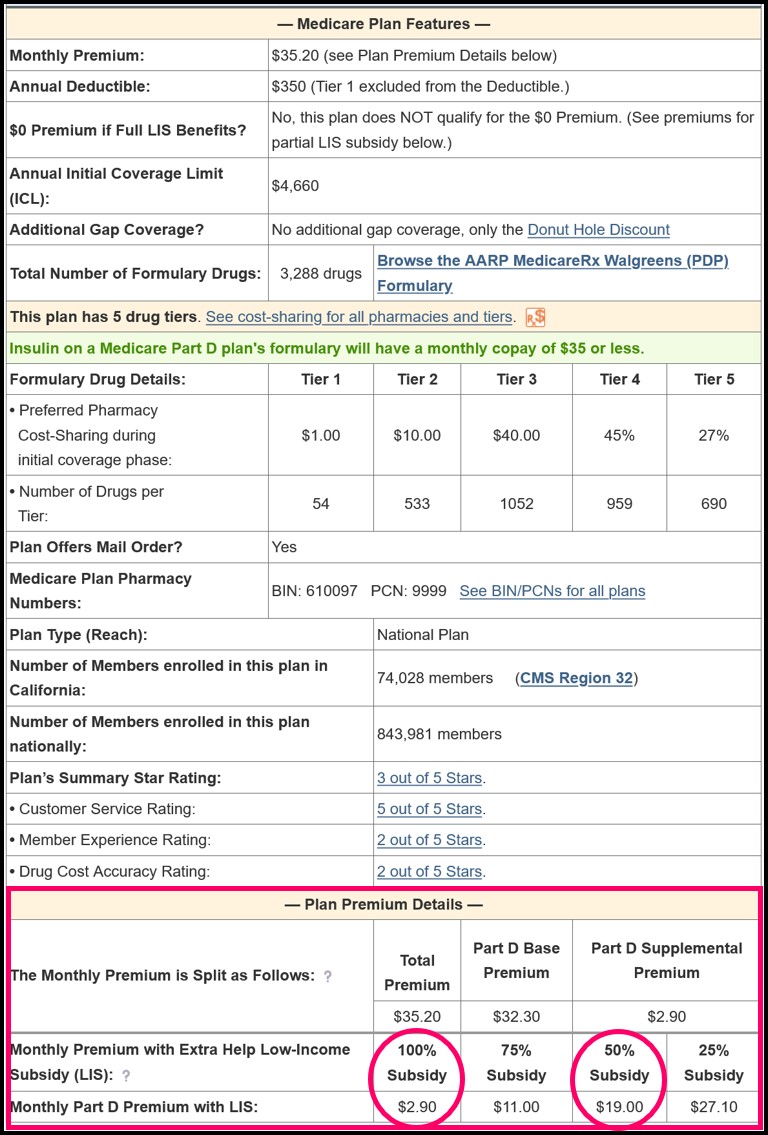
Older Pre-2024 Example: Here is a similar example from 2023 using a larger Part D plan premium (although we no longer have partial LIS in 2024). In 2023, California had an LIS benchmark premium of $38.86, and, assuming the person is qualified for full Extra Help benefits and decides to join the 2023 AARP MedicareRx Walgreens (PDP) that had a $35.20 monthly premium, the person may expect to have a $0 premium for the plan since the $35.20 premium is below the 2023 California benchmark.
However, as shown on our PDP-Finder plan details page, the person would actually pay a monthly premium of $2.90 because this 2023 Part D plan has "enhanced" features and does not qualify for the $0 premium even though the $35.20 premium is less than the $38.86 benchmark.
Question: Where can I see if a Medicare Part D plan qualifies for a $0 LIS premium?
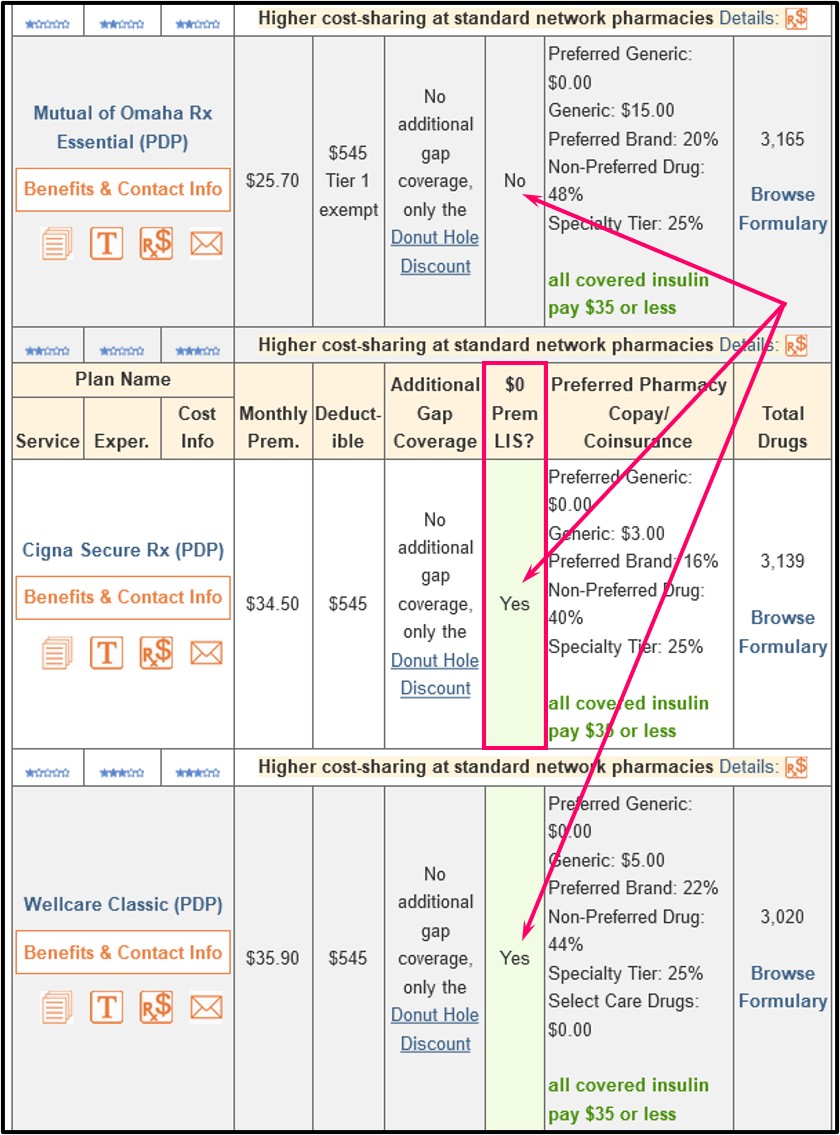
You can see whether a Medicare Part D plan qualifies for your state’s $0 LIS premium using our Medicare Part D Plan Finder where all Part D plans available in each state are shown and LIS $0 premium plans are noted.
Here is an example link to the stand-alone California Medicare Part D plans (you can choose a link to view plans in another state): PDPFinder.com/CA. You will notice on the PDP Finder results page that the column showing "$0 Prem LIS?" is marked with "Yes" and a mint-green background for qualifying plans.
Q1Medicare PDP-Facts shows plan type
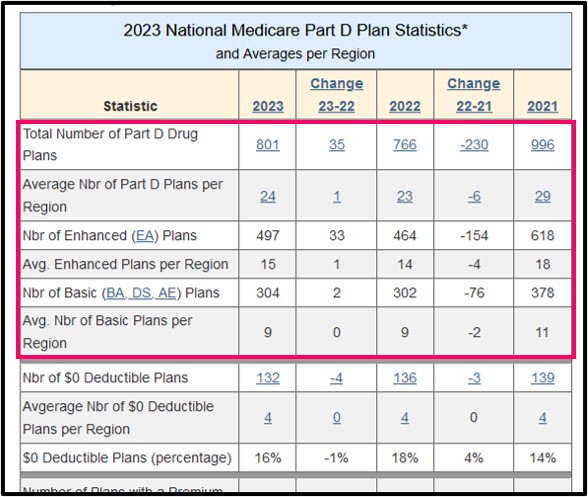
As a note, when new plan designs are released each year, we summarize the annual number of Medicare Part D plans into Medicare Part D benefit types and this information is shown in PDP-Facts.com, our online annual summary of stand-alone Part D Plan statistics (National and State). Here is an example PDP-Facts screen showing changes from 2021 to 2022 to 2023. From the graphic you can see the total number of standard Medicare Part D plans (PDP only) vary year-to-year along with changes in the type of Medicare Part D plans that are offered each year.
See: Prescription Drug Benefit Manual, Chapter 5: Benefits and Beneficiary Protections, (Rev. 14, 09-30-11)
As a note, when new plan designs are released each year, we summarize the annual number of Medicare Part D plans into Medicare Part D benefit types and this information is shown in PDP-Facts.com, our online annual summary of stand-alone Part D Plan statistics (National and State). Here is an example PDP-Facts screen showing changes from 2021 to 2022 to 2023. From the graphic you can see the total number of standard Medicare Part D plans (PDP only) vary year-to-year along with changes in the type of Medicare Part D plans that are offered each year.

See: Prescription Drug Benefit Manual, Chapter 5: Benefits and Beneficiary Protections, (Rev. 14, 09-30-11)
Browse FAQ Categories
Q1 Quick Links
- Sign-up for our Medicare Part D Newsletter.
- PDP-Facts: 2024 Medicare Part D plan Facts & Figures
- 2024 PDP-Finder: Medicare Part D (Drug Only) Plan Finder
- PDP-Compare: 2023/2024 Medicare Part D plan changes
- 2024 MA-Finder: Medicare Advantage Plan Finder
- MA plan changes 2023 to 2024
- Drug Finder: 2024 Medicare Part D drug search
- Formulary Browser: View any 2024 Medicare plan's drug list
- 2024 Browse Drugs By Letter
- Guide to 2023/2024 Mailings from CMS, Social Security and Plans
- Out-of-Pocket Cost Calculator
- Q1Medicare FAQs: Most Read and Newest Questions & Answers
- Q1Medicare News: Latest Articles
- 2025 Medicare Part D Reminder Service
